
Real Image digitizing is the process of converting an ordinary image or artwork into a digital format that embroidery machines can understand and recreate onto fabric. This process is important in the art of embroidery as it allows for complex and detailed designs to be accurately translated onto fabric.
Real Image digitizing involves using specialized software to convert the image into a series of stitches and commands that the embroidery machine can follow. This ensures that the stitches on the fabric are perfect and outcome of the artwork is stunning.
It plays an important role in the embroidery process because it helps to maintain the quality and accuracy of the embroidered pattern. True Digitizing specializes in delivering high-quality real image digitizing, maintaining your designs are accurately converted into digital formats for perfect embroidery results.
When it comes to real image digital transformation, there are many ways to gather and convert real images or documents to digital formats. These methods employ scanners, cameras, or specialized software to collect and transform the original image's details precisely.
People and groups can use these strategies to maintain and spread valuable visual information in a more accessible and easy digital format.
In this blog post, we will explore some of the most common techniques for real image digitizing. Such as scanning, photography, and software-based methods. We will discuss the advantages and limitations of each technique, as well as provide tips for achieving high-quality results.
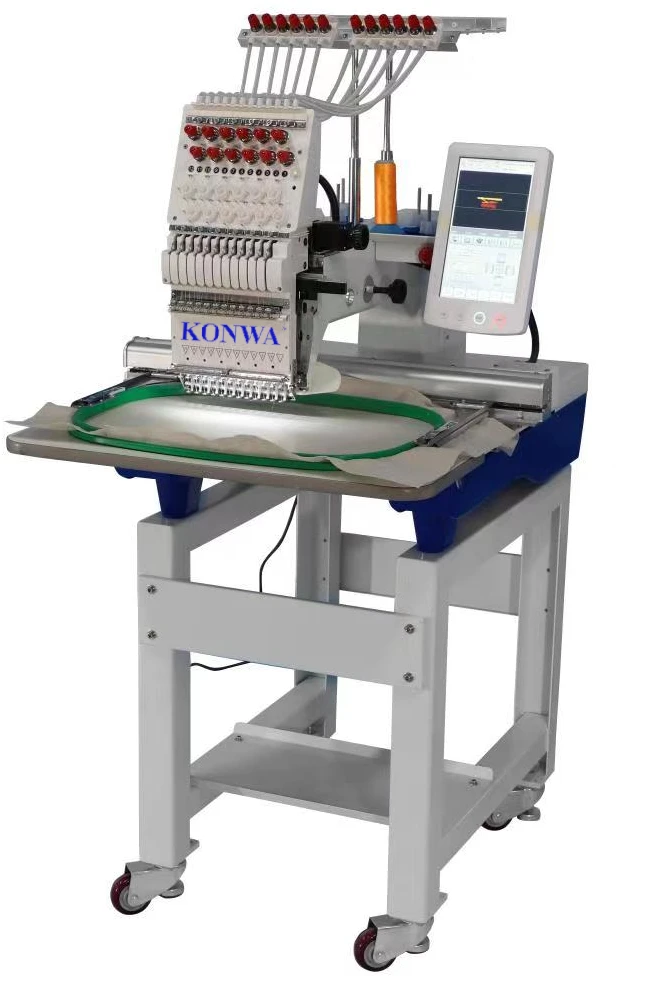

Choosing the right equipment for a project involves considering the specific needs of the project, the technical requirements, and budget constraints. It is essential to prioritize long-lasting, and performance to ensure the selected equipment can handle the demands of the task at hand.
Durability is important to ensure the equipment can withstand the rigors of the project. While performance is necessary to achieve the desired outcomes efficiently. Versatility allows the equipment to adapt to different project requirements, maximizing its utility.

Several primary factors affect digital picture quality, including bit depth, resolution, and the technology used to digitize genuine images. Bit depth defines the number of colors that a digital image may display, whereas resolution affects the amount of detail and sharpness. The real image digitizing method, such as scanning or digital photography, also impacts the overall quality of the image.

To make adjustments to digital images based on the resolution, bit depth, and sampling of the original analog material. First, you need to understand these terms.
Resolution refers to the number of pixels per inch. Bit depth refers to the range of color values, whereas sampling refers to the number of measurements performed per unit of time. When changing photographs, it is essential to consider how an image differs from its real-world size. This can be handled by setting the physical print size and resolution.

When working with paper backgrounds and color palettes, it is important to separate the artwork from its background. This can be done by using the White Point Eyedropper Tool under adjustments levels to adjust the white point of the image and then deleting the background. Additionally, adding a new white-fill background layer is important for better visualization of the artwork and color palettes.
The process of real image digitizing has become increasingly important. Whether it's for professional use or personal archiving. Converting physical photographs or documents into digital format gives numerous benefits. However, it's important to approach this process with care and attention to detail to ensure that the digital copies are of high quality and accurately represent the original images.
These tips will guide anyone looking to successfully transition from physical to digital images whether you're a professional embroiderer, a family archivist, or someone looking to digitize important documents. These guidelines will help you make the most of the digitization process.
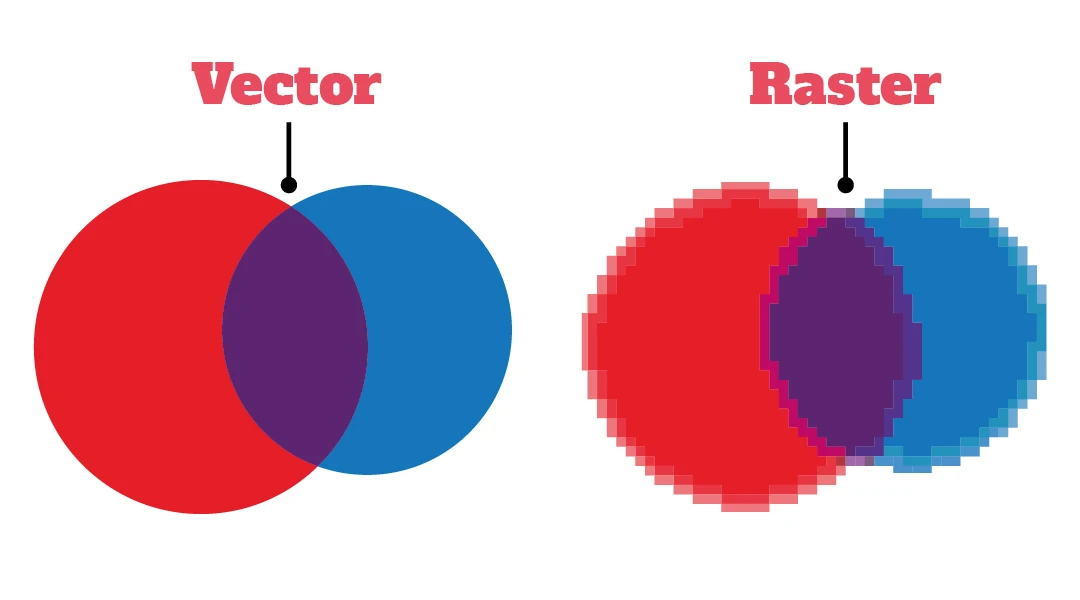
Vector images are composed of mathematical equations and are scalable without losing quality. Making them better for designs that need to be resized. They are also easily editable as individual elements can be manipulated. On the other hand, raster images are composed of pixels and become pixelated when resized, making them less suitable for scalability. Using vector graphics software, embroidery designers can create artwork that can be scaled infinitely without any loss of quality.
Raster images may lose quality when resized. The advantage of vector images lies in their scalability and editability. While raster images excel in detailing and realistic representations.
For projects that require scalability and editability, such as logos and illustrations, vector images are recommended. For projects that prioritize high detail and realism, like photographs, raster images are more suitable.
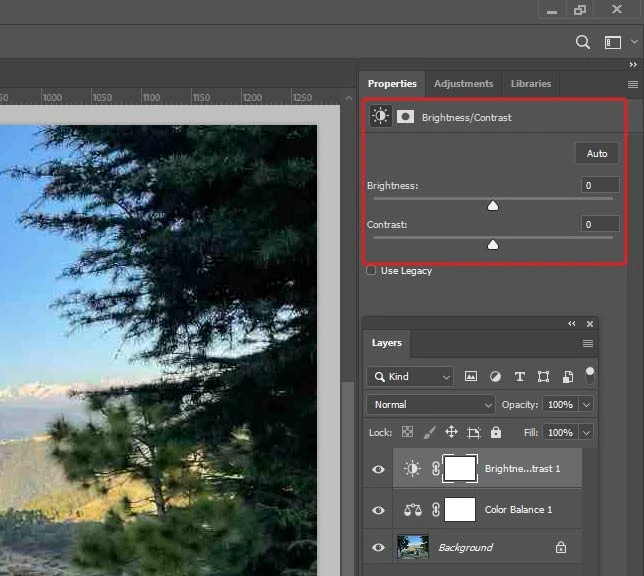
In Photoshop, maximizing image quality and size for digitizing involves several key steps. First, it's important to increase contrast, adjust levels and curves, and condense layers to achieve clear and detailed designs. This can be done by using the contrast and brightness tools, adjusting the black and white points in the levels, and fine-tuning the tonal range with the curves tool.
The relationship between dots per inch (DPI) and file sizes is important to evaluate picture quality and storage needs. DPI refers to the resolution of an image, and higher DPI settings result in larger file sizes as they contain more information and detail.
Resolution breakpoints such as 300 DPI for print and 72 DPI for web affect the quality and storage needs of images. Additionally, different file formats also impact file sizes and image quality. With uncompressed formats like TIFF producing larger files with higher image quality compared to compressed formats like JPEG.
When scanning images, selecting higher DPI settings and uncompressed file formats will result in larger file sizes but better image quality. Lower DPI settings and compressed formats will lead to smaller file sizes with reduced image quality.
Understanding how DPI and file formats affect image quality and storage needs is important for effective digital photo storage and preservation.
Embroidery digitizing is the process of capturing complex designs and detailed artworks for conversion into digitized embroidery. This involves choosing designs and refining them before transforming them into digital files. Techniques such as using vector images, precise stitching instructions, and consideration of fabric and machine capabilities are used to capture the essence of the original design. Vector images are important for maintaining the complex details of the artwork. While precise stitching instructions ensure the design is accurately replicated.
Understanding the skill of real-image digitization is important for creating perfect embroidered designs. From choosing the appropriate equipment to using scanning processes and optimizing digital files, every step plays an important role in maintaining the intent of the original image. Whether you're a professional embroiderer or a person digitizing significant memories, the guidance provided ensures a smooth transition from physical to digital media.
Transform your custom embroidery designs with our expert skills and discover all the possibilities of your digital artwork. Explore the world of embroidery services today and convert your vision into a magnificent reality.
Nick William has been immersed in the world of embroidery digitizing for over 20 years, earning 25 industry awards throughout his career. As a 3rd generation embroidery expert, Nick’s journey started in his family’s workshop, where he learned the art of digitizing before the rise of modern software. He has worked with leading commercial embroidery businesses and has shared his expertise with over 75,000 home and professional embroiderers. As an author at True Digitizing, Nick is passionate about teaching others how to create beautiful, precise designs through easy-to-follow tutorials and expert advice.
Categories

How To Create A Vector File: Step-by-Step Guide
15-04-2025

What Is A Vector File? Everything You Need To Know
14-04-2025

Best Janome Embroidery Machines You Need to Check Out in 2025
11-04-2025

Custom Embroidery Digitized Designs For Hoodie Lovers
10-04-2025

Best Embroidery Patches For Your Clothes
10-04-2025

Professional Online Photo Digitizing Services Provided by True Digitizing
09-04-2025

Best Babylock Embroidery Machines For You
09-04-2025

Barudan Embroidery Machines: From Beginners to Professionals
04-04-2025

Custom Sweatshirt Embroidery Digitized Designs By True Digitizing
03-04-2025

Why Brother Embroidery Machines are the Best Choice for Embroiderers?
27-03-2025